How to Prepare Your Body and Mind for a Healthy Pregnancy
Preparing for pregnancy is one of the most important steps toward ensuring a healthy journey for both you and your future baby. Taking proactive measures, both physically and mentally, can improve fertility, reduce pregnancy complications, and boost your overall well-being. Studies show that preconception health directly impacts maternal and infant outcomes (CDC: Preconception Health).
In this guide, you’ll discover essential steps to optimize your body and mind, including nutrition, exercise, mental health strategies, and lifestyle adjustments—empowering you to start your pregnancy journey with confidence and vitality.
Schedule a Preconception Checkup

Visiting a healthcare provider before trying to conceive is a crucial first step. A preconception checkup allows you to review your medical history, discuss any current medications, and ensure your vaccinations are up to date.
It’s also an opportunity to identify potential health risks, such as chronic conditions or genetic concerns, that could affect your pregnancy. Early detection and management of these issues can pave the way for a smoother journey ahead. For more information on preparing for your visit, see the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Preparing for Pregnancy.
Optimize Your Nutrition
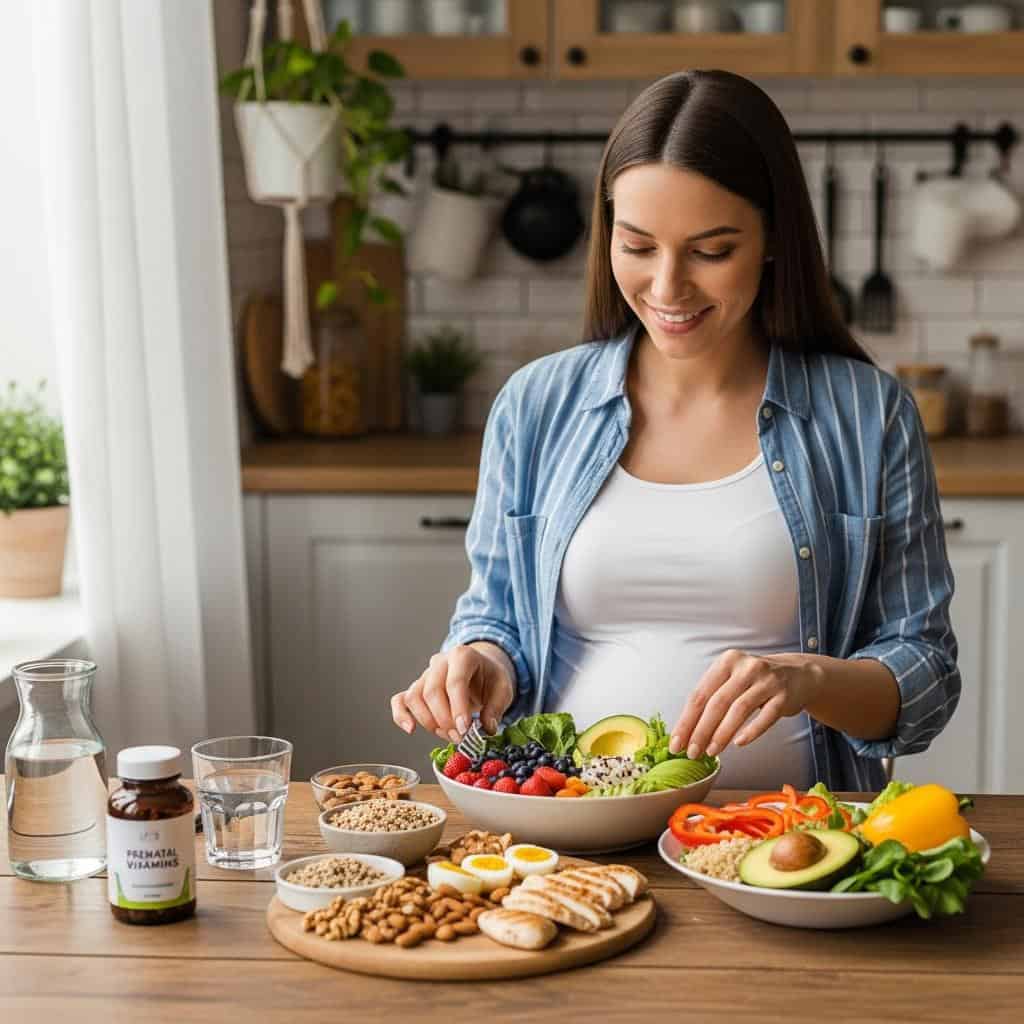

Adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet is vital for supporting fertility and healthy fetal development. Focus on consuming a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Key nutrients such as folic acid, iron, and calcium are especially important—folic acid helps prevent neural tube defects, while iron supports blood health and calcium strengthens bones. Consider starting a prenatal vitamin as advised by your healthcare provider. For detailed nutrition guidelines, visit the CDC: Preconception Nutrition.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
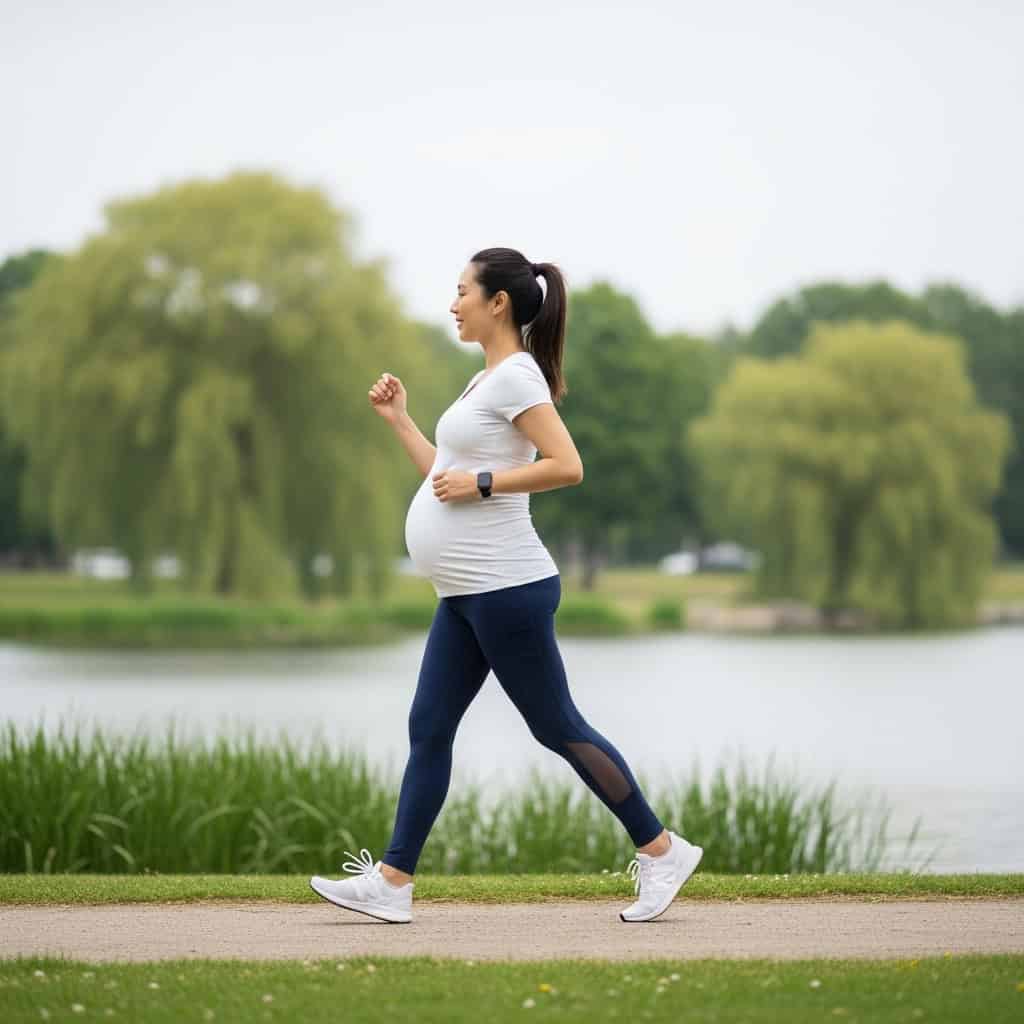

Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve your chances of conception and lead to better pregnancy outcomes. Being either overweight or underweight may disrupt hormonal balance and fertility, and can increase the risk of complications such as gestational diabetes or preeclampsia.
Aim for a healthy BMI by incorporating regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or swimming, and practicing mindful eating habits. Focus on portion control and nutrient-dense foods. For guidance on healthy weight and pregnancy, refer to the March of Dimes: Healthy Weight in Pregnancy.
Manage Stress and Mental Health
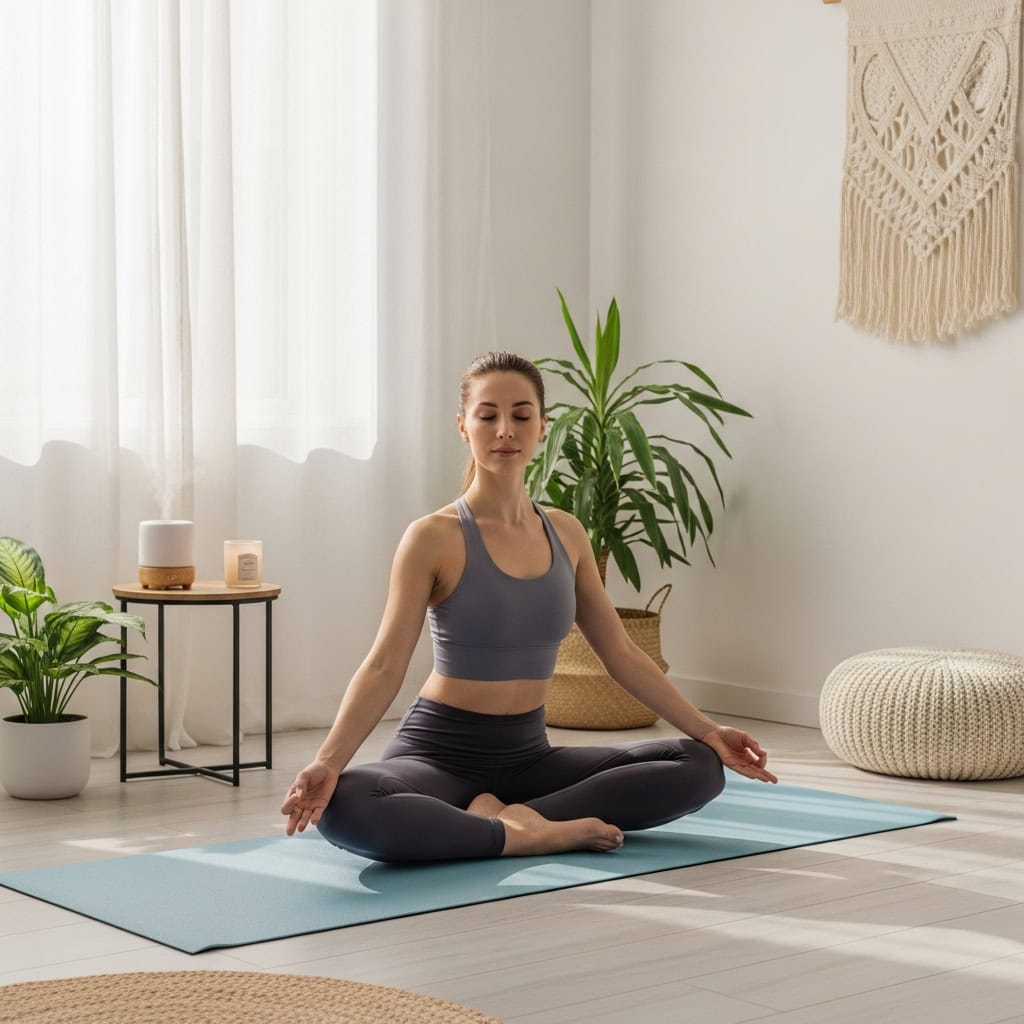

Emotional well-being plays a critical role in preparing for pregnancy, as high stress levels can affect fertility and overall health. Prioritize stress management by practicing mindfulness techniques such as meditation or yoga, establishing regular self-care routines, and seeking support from friends, family, or professional counselors if needed.
Addressing mental health concerns early helps foster a positive mindset and coping skills for the journey ahead. For more tips on managing stress and preparing emotionally, visit Mayo Clinic: Preparing for Pregnancy.
Eliminate Harmful Substances
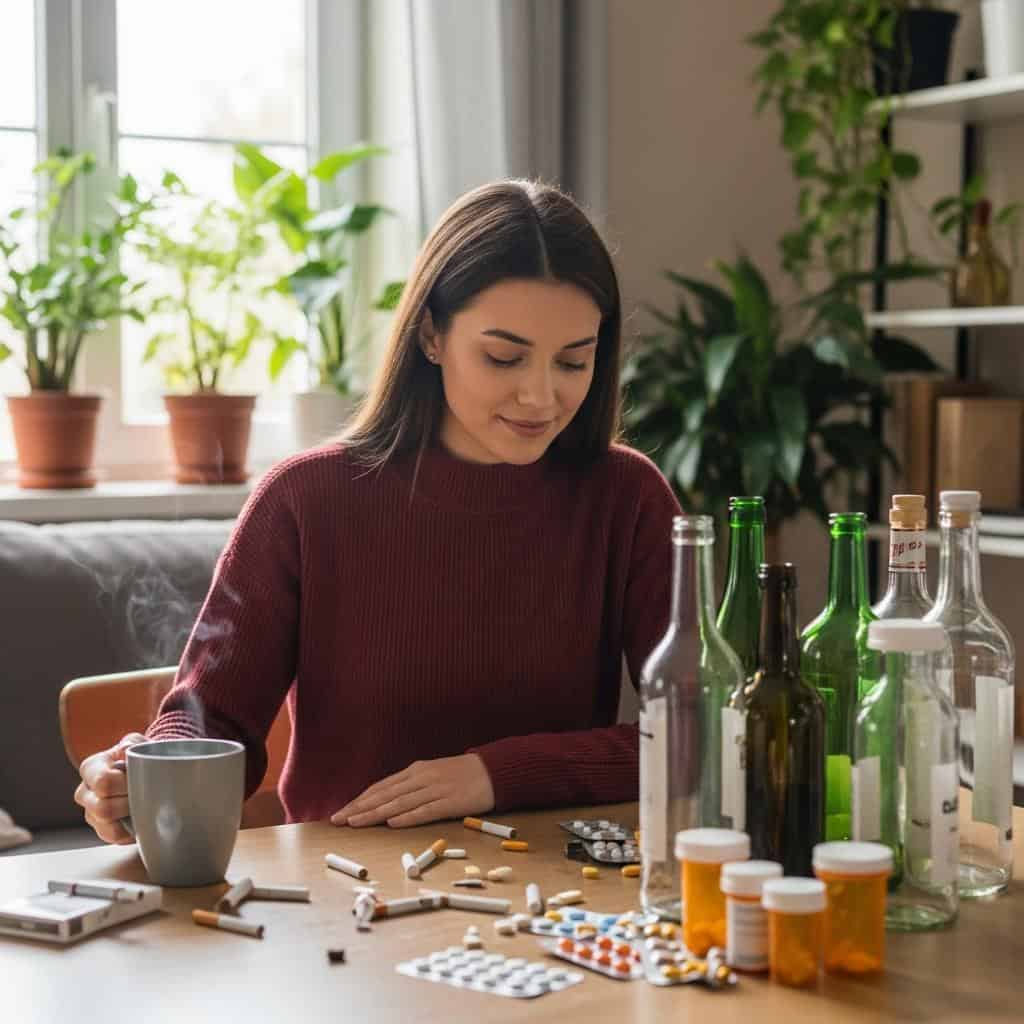

Avoiding tobacco, alcohol, recreational drugs, and limiting caffeine intake is essential for boosting fertility and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. These substances can negatively impact reproductive health, increase the risk of birth defects, and cause complications during pregnancy.
If you smoke or use other harmful substances, seek support through cessation programs or counseling. Gradually reduce caffeine to under 200 mg per day, as recommended by experts. For practical tips and resources on quitting, visit Office on Women’s Health: Preconception Health.
Review and Adjust Medications

It’s important to evaluate all current medications with your healthcare provider before trying to conceive. Some prescription and over-the-counter drugs, as well as herbal supplements, can affect fertility or pose risks to a developing baby.
Your provider can help you identify which medications are safe, suggest safer alternatives if needed, and adjust dosages appropriately. Never stop or change medications without professional guidance. For more information on medication safety and preconception planning, consult the FDA: Medicines and Pregnancy.
Prioritize Sleep and Physical Activity

Regular, moderate exercise and quality sleep are essential for hormonal balance, energy, and overall health during preconception. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as walking, cycling, or yoga, to promote circulation and reduce stress.
Establish a consistent sleep schedule, aiming for 7-9 hours per night, and create a restful environment by limiting screen time before bed. These habits help prepare your body and mind for pregnancy. For further guidance, explore Sleep Foundation: Healthy Sleep Tips and ACOG: Exercise During Pregnancy.
Build a Supportive Environment

Establishing a nurturing and supportive environment is vital as you prepare for pregnancy. Engage in open communication with your partner and loved ones about your goals and emotional needs. Involving your partner in healthy lifestyle changes and decision-making fosters teamwork and reduces stress.
Seek out community resources, such as local support groups or online forums, for additional encouragement. Building a strong support network can help you navigate challenges and celebrate milestones. For more tips on strengthening relationships and finding support, visit March of Dimes: Planning for Pregnancy.
Conclusion

Preparing your body and mind for pregnancy lays the groundwork for a healthy, positive experience for both you and your future baby. By following essential steps—such as scheduling a preconception checkup, optimizing nutrition, managing stress, and building a supportive environment—you can boost fertility, reduce risks, and enhance overall well-being.
Be proactive and informed, and don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance tailored to your unique needs. Your journey toward parenthood starts with thoughtful preparation. For more comprehensive preconception resources, visit CDC: Planning for Pregnancy.